- ... Gregorian.1
- The prime examples among 8-meter-class
telescopes are the Magellan telescopes, which have an f/11 Gregorian
secondary.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... detector2
-
Anamorphic demagnification
comes from the relation of incident to diffracted angles.
At fixed wavelength,
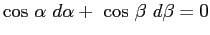 .
If the grating tilt is set up such that
.
If the grating tilt is set up such that
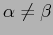 ,
then
,
then
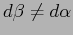 . Astronomical spectrographs
are typically configured so that
. Astronomical spectrographs
are typically configured so that
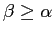 and
and
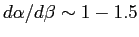 . The diffracted beams from the
slit are spread over a smaller angle than the incident beams were, and the
slit is demagnified at the detector. This affects the translation
of slit size into spectral resolution, giving higher resolution
by
. The diffracted beams from the
slit are spread over a smaller angle than the incident beams were, and the
slit is demagnified at the detector. This affects the translation
of slit size into spectral resolution, giving higher resolution
by 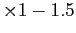 than we will calculate for the simple case. See
Schweizer (1979, PASP, 91, 149) for a detailed explanation.
than we will calculate for the simple case. See
Schweizer (1979, PASP, 91, 149) for a detailed explanation.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.